“Data Driven” as a key word is not new. Success stories of implementing a data driven culture or creating successful “Data Products” is still new. We will continue to look at my proposed enterprise data management and high level lego framework in this article and focus on “Data Mission” Level 2.
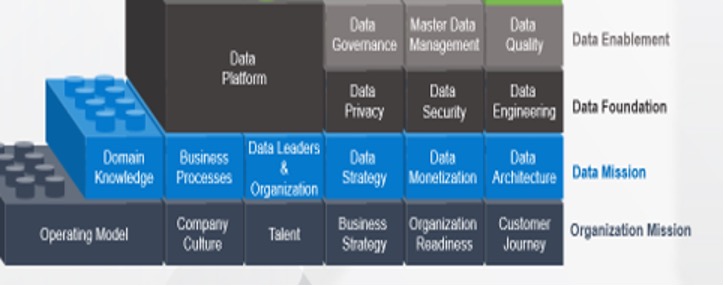
The recommended Lego blocks on enterprise data management visual are stacked 7 blocks high beginning with Level 1: Organization Mission, continuing onto Levels 2-6 Data Mission, Data Foundation, Data Enablement, Data Decisions, Data ROI and ending with Data as an Asset as Level 7 at the top. In the upcoming articles, we will review each of these 7 levels in detail as part of this quarterly column.
The 7 levels of the Lego framework drive towards the ultimate goal of Data as an Asset (DaaA), :evel 7 by enabling data driven culture and the mindset to create successful data products. In the prior column on this topic, we reviewed the “Organization Mission” Level 1 in detail with Operating Model, Organization Readiness, Business Strategy, Talent, Company Culture and Operating Model as foundational pieces that make the Organizational Mission, Level 1 of the framework.
Let’s review the “Data Mission” Level 2 and the relationship to organization mission Level 1 and the “Data Foundation” Level 3 as part of this article.
Data Architecture drives decisions on technology towards managing data and business needs. Detailed analysis on what data is needed in the organization, when and how the data is acquired, how the data is stored and protected are all part of this critical data discipline. Decisions on data engineering tools and technology, cloud platforms, data privacy and security tools along with creation of data modeling governance are all part of services of data architecture team. Data Architecture lays down the blueprint for data foundation and data enablement levels as depicted in the framework.
The frameworks visualize the key characteristics of a successful data architecture discipline that entails being business-driven with focus aligned on customer journey, flexible and scalable with respect to data engineering and very tightly aligned with data privacy and data security requirements. Data protections to prevent unauthorized data access and improper use of data is paramount for building the trust of customers to sell “trusted” data products.
Data Monetization is the driving force behind being data drive company. The concept and process of utilizing data from within the enterprise along with external data to drive operational excellence internally or to drive more revenue is Data Monetization. Data itself is considered as an output of business processes, leveraging this output as input to create data products is more mindset and cultural change than the process or technology behind it. In the proposed framework organizational readiness Lego block supports this key concept of data monetization Lego block.
Data monetization can be internal or external and direct or indirect. In the case of internal, the data is used directly to make measurable business operational performance improvements like reducing customer care time or manufacturing process times. In external data monetization, the data is used directly to increase revenue as a product or in exchange of service or products. Data Monetization has to work in the constraints of data privacy and data security and thus supports these Lego blocks in the proposed framework.
Data Strategy is the guiding path and a dynamic iterative key process to become data driven as an organization. Data strategy defines the why, what, how for all data that is needed by the organization towards supporting the business objectives. In the proposed framework data strategy, Lego blocks sits over the Business strategy block for this very reason.
Decisions on data acquisition, ingestion, analysis, funding of data initiatives, delivery of data return on investments are all considered part of a comprehensive data strategy. Frameworks of “defensive” and “offensive” data strategies have come into existence specific to the organization and the outside influencing factors like political climate, interest rates, regulations etc. There is need for data strategy to be agile with regular documentation of decisions about any trade-offs on any proposed or chosen approach. In many cases, these decisions will be details like harmonized, cloud enabled, regional or business line owned, single source vs multi source and may include specific organization level data gaps or opportunities defined.
Data Leaders & Organization executes the Talent strategy towards the goal of being data driven. Organizational structure options like functional, divisional, matrix, capability or other types are all enabling decisions for data mission level to be activated.
Data organization needs to be “purpose and time specific” to the organization. For example, in many cases, the data organization leaders will report into information technology if the need of the organization is to accelerate the data foundation Level 3 processes of data platform and data governance. In cases where organization is in a very regulated industry data leadership and talent may be focused as part of a chief risk or compliance officer, data leaders and organization need to enable data driven culture while managing constraints of overall organization mission and organization way of working that may vary by departments, chain of command, span of control mindset.
Business Processes in the context of enterprise data management is the key towards understanding the data created by the business processes. The relationship between people, processes, technology needs to be analyzed in terms of data value chains. Key enterprise data management processes like data linage, data traceability, canonical data models, data value chains etc. are all part of the business processes Lego Block as defined in this framework. Data business processes drive the need for data platforms and hence the decisions on what types and how much investment is needed in what specific data platform technologies.
Domain Knowledge is the sum of experiences that need to be tracked and documented as business processes are enabled towards organization mission. Domain knowledge is industry specific, business process, global region, etc. specific and becomes a key input into enterprise data mission.
“Data as an Asset (DaaA) or an organization is only possible with domain specific experts who understand, respect and care for data as a raw material towards enabling data driven culture. In many cases, domain knowledge on data initiatives reflects the level of expertise required in specific data science domains like fraud detection, targeted advertising, next best action recommendations etc.
Summary
Data Mission is a key layer as proposed in the Enterprise data management Lego framework. There 6 critical blocks (Data Architecture Data Monetization, Data Strategy, Data Leaders & Organization, Business Processes and Domain Knowledge) makes Data Foundation a needed layer for any enterprise. Data Mission drives and provides acceleration as needed to set up data driven culture. It focuses on the why and what from a data point of view to accomplish organization mission.