I recently presented a seminar at an event called “Data, the Vital Organisational Enabler” Information is at the Heart of ALL of the Business during which I raised the question,
I recently presented a seminar at an event called “Data, the Vital Organisational Enabler” Information is at the Heart of ALL of the Business during which I raised the question,
“Is the data asset really that much different from other assets?”
We often hear it said that Data is an asset, it’s got to be managed, few people in the business understand us who do, and so on.
Don’t get me wrong, I’m not trying to cast any doubt on the importance of data as an asset, but I wanted to raise the level of debate from a subliminal nod to a conscious examination of the characteristics of different “assets” and to compare them with the ‘Data asset”.
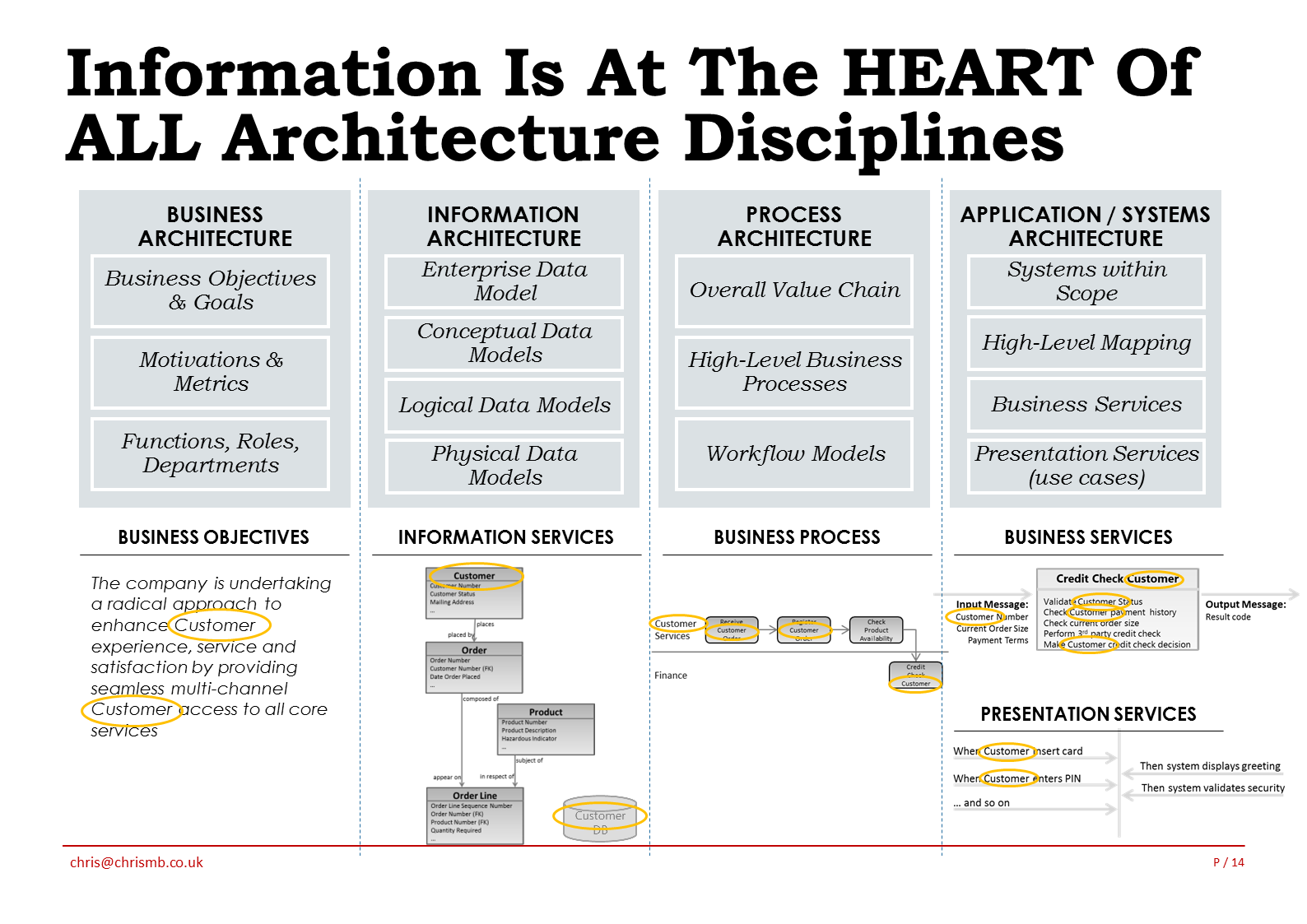
Firstly, let me re-iterate that Information IS absolutely at the heart of the business, my recent white paper talks at some length about this and the diagram here briefly illustrates 4 business architecture disciplines & the vital role of data in each of these.
However, what I want to raise here is just what are some of the characteristics of core assets in the business? And, if as we all say data IS one of those key assets, how, do these characteristics differ in the “Data asset” compared with other the other assets that we frequently encounter in our organisations, if they differ at all?
So first of all let’s have a think about some other “assets”?
I have selected 7 other assets many of which are regularly seen across a variety of businesses, and I have tried to compare them with the “Data Asset”.
The assets I’ve selected for this comparison are:
- Oil
- Money
- Blood
- People
- Property
- Materials
- Intellectual Property (IP) and of course
- Data.
The characteristics of the assets themselves required more consideration.
After much thought and batting the notion around with others I settled upon these 5 characteristics:
- Is the asset Copyable? i.e. without resorting to the realms of science fiction “replicator” machines
- Does use of the asset in some way deplete it?
- Is it a straightforward, and/or usual practice to ascribe a monetary value to the asset?
- Is the asset a real, tangible thing, or an abstract concept?
- Does the asset have to be processed in some way to yield value?
Now, I’m sure that I could have come up with further asset types and asset characteristics, and I may well do so as this analysis develops, but for now these are the ones that I start with.
Analysis
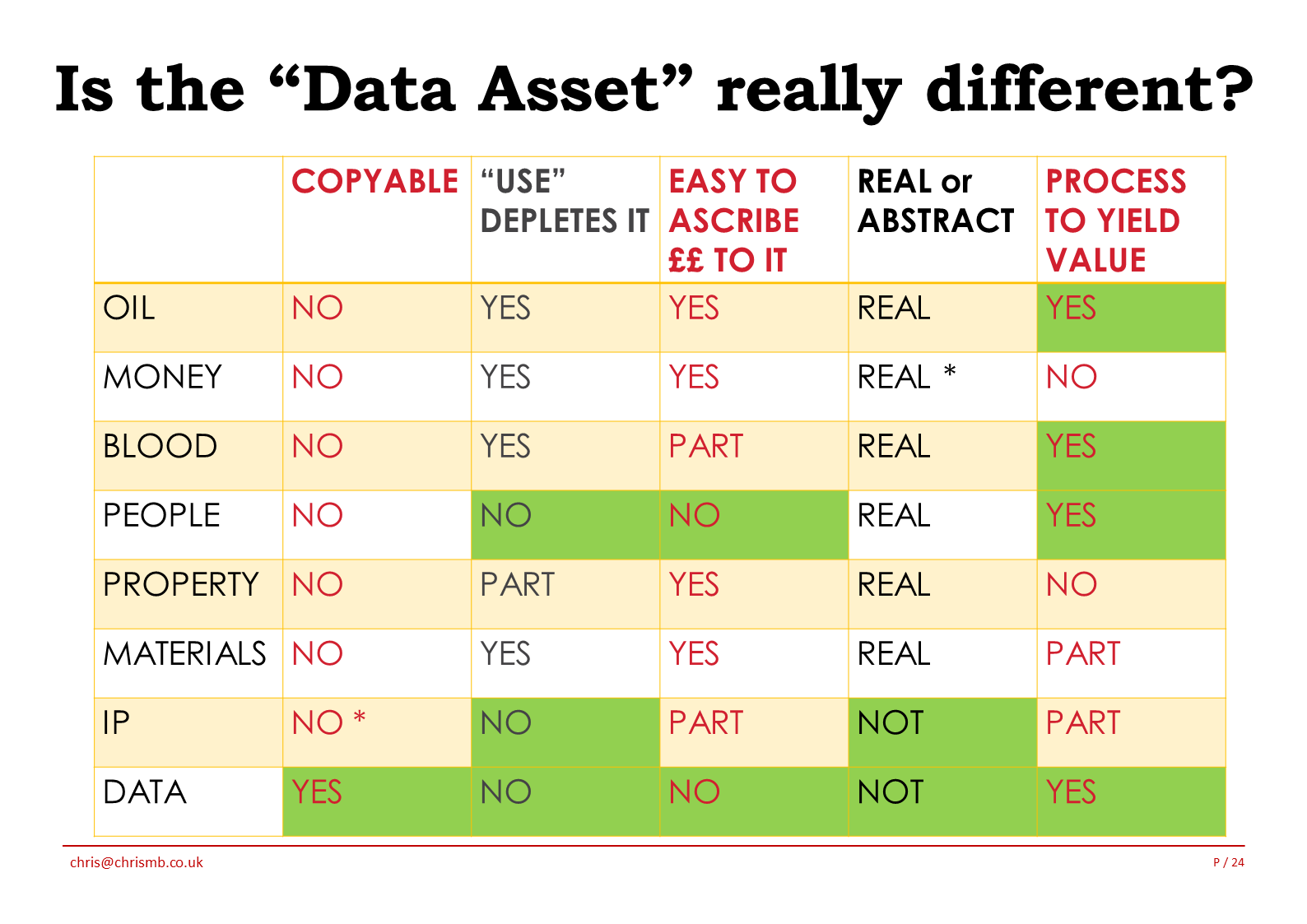
So let’s analyze these assets against the characteristics & see what (if any) conclusions we can draw from it?
Oil
Oil is not copyable, and most definitely using it depletes it. It is definitely usual practice to give a value to oil (the $50 barrel for example) and it is a real concept. Finally it has to be processed to be turned into something useful like petrol, diesel or plastic.
Money
So you can’t (legitimately) copy money, and as I know all too well with two sons at University, using money depletes it, and naturally you give a value to money. It’s mostly a real concept being underpinned by Gold stock, and doesn’t have to be “processed’ to deliver value.
Blood
Blood isn’t copyable in the mainstream (although as we speak blood substitutes are being trialled), and use of it depletes it (it has to be re-cleaned & oxygenated after use). It’s not too difficult to ascribe a value to it, and it is a real concept. Finally it has to be processed by our organs to yield value.
People
People as we know them are not copyable (although biological cloning is possible). I’ve said that use of people does not deplete the resource as we can apply our skills & intellect many times. However, people do age and limbs and minds fade so perhaps this should be answered as “partly true”. It’s not widespread practice to ascribe a monetary value to a person except in a few cases (e.g. professional sportsmen). People are real and without trying to get too philosophical, they have to do something to yield a value.
Property
Property such as buildings are not copyable. Sure, you can have a plan for a building & use that several times, but its using different bricks, is on a different site and so on. The Eiffel Tower in China is a fake! Using a property does slowly erode it, things wear out and need to be maintained. Property does have value & it’s usual practice to give it such. Property is a real concept, but doesn’t have to be processed to generate value.
Materials
So here I’m talking about raw materials. Again, without a sci-fi replicator they are not copyable, and just like a match the act of using them depletes them. Most materials have a monetary value easily ascribed to them, for several that’s the basis of the commodities market. They are not abstract things and for the most part have to be processed to yield a value.
Intellectual Property (IP)
IP is not legally copyable. IP thrives on being reused, so is not depleted by use. There is frequently a monetary value allocated to IP, and much like a thought or an idea it’s mostly an abstract concept. Finally, IP must be used (processed) to gain real value from it.
Data
So what about data; how does this stack up against the asset characteristics?
Data is copyable; with digital media any number of copies can be taken without the data being degraded. Using data does not erode it or make it wear out. Sure, the relevance of the data may decrease over time, but it does not wear out. While there is much talk about “monetizing” data, this is still not a widespread practice but will no doubt become so in the future. Data is an abstract concept, as it represents something beyond itself. Data needs to be utilized by processes to have value (and conversely processes must have data to operate upon).
Conclusion
Having looked at these 8 different assets, and the 5 characteristics is there anything that jumps out at us?
If we look for assets which have the same values of characteristics as those for the “data Asset” then we’re going to be disappointed.
Of the 5 characteristics, 3 of the assets (Money, Property and Materials) have zero common values with Data.
2 of assets (Oil and Blood) have one common characteristic value shared with “Data”.
Intellectual Property (IP) has two common characteristics.
Heading the pack with three common characteristics is the People asset.
It’s interesting to note though, that there aren’t any of the assets that share 4 let alone 5 of the characteristics as we see in Data.
 Thus it is probably reasonable to conclude that:
Thus it is probably reasonable to conclude that:
The Data Asset IS different to other business assets that we encounter.
Furthermore, as described in my white paper all of the business depends upon data for its wellbeing.
Unfortunately, we still encounter organizations where the various disciplines of Information Management are not understood (or more frighteningly are knowingly not addressed).
Indeed, Professor Joe Peppard wrote “The very existence of an organization can be threatened by poor data quality.”
If, as we suggest here, it is different, then the management of the data asset requires specific skills and capabilities; enter the Information Professional.
Wise organizations are realizing that Information really IS a vital asset, it IS worthy of being managed professionally, and yes it IS different.