This is part two of a two-part article by Melanie Mecca and Jim Halcomb of the CMMI Institute about the Patient Demographic Data Quality (PDDQ) Framework. In part one, we introduced the framework, shared with you the maturity model from which the framework is based and who may benefit from it, and shared what is inside the framework. In part two, we will cover what is evaluated as part of the framework, how the framework is intended to be used, and how you can access the framework.
This is part two of a two-part article by Melanie Mecca and Jim Halcomb of the CMMI Institute about the Patient Demographic Data Quality (PDDQ) Framework. In part one, we introduced the framework, shared with you the maturity model from which the framework is based and who may benefit from it, and shared what is inside the framework. In part two, we will cover what is evaluated as part of the framework, how the framework is intended to be used, and how you can access the framework.
Assessing data management capabilities is a strategic initiative which can yield significant benefits over time. Evaluating current practices against the PDDQ Framework also reveals numerous actionable, tactical initiatives that can be accomplished by leveraging organizational strengths and making practical, sensible modifications to existing processes.
The PDDQ Framework’s embedded path of successive improvement guides adopters in their work to establish and roll out activities needed to achieve and benefit from effective data management practices. Dependencies exist but are addressed in the test, because each Process Area is designed such that it can be evaluated separately.
For evaluation purposes, answers to the key questions are recorded and given a value in the accompanying scoring mechanism. The introduction to each process area and the explanatory content following the key questions provide additional context for which to interpret the question.
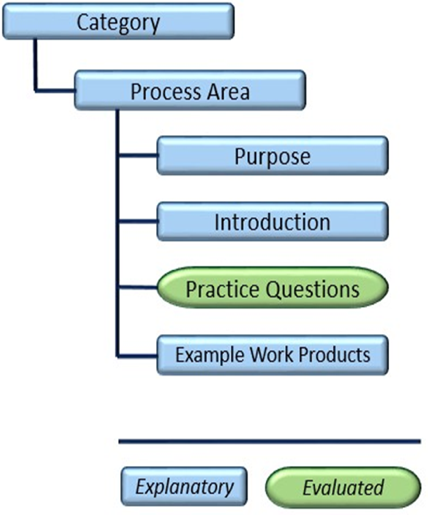
Collectively, example work products help the organization determine the extent to which processes are currently defined and being followed. The work products, functionally described, provide insight into typical artifacts – documents, templates, mechanisms, metrics, etc. – which are created as processes and developed, established, maintained, and improved. They are presented as helpful examples for the organization to consider.
Key questions, reflecting capabilities within a process area, are organized in successive levels of achievements, are synthesized from the experience of hundreds of organizations over the past three decades.
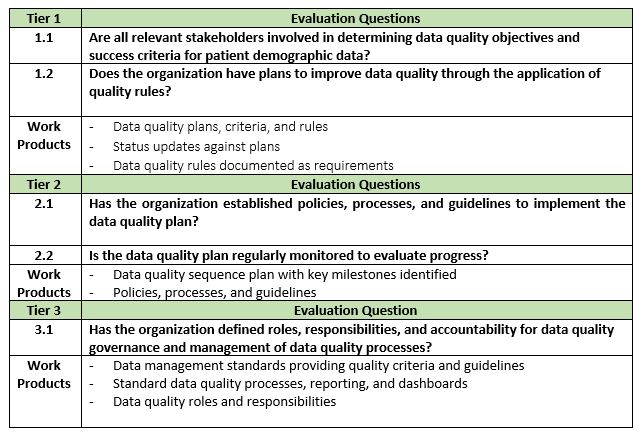
The PDDQ Framework organizes these progressive levels in ‘Tiers.’ Tier 1 – Foundational addresses capabilities that are typically accomplished first, Tier 2 – Building questions target capabilities that build on the foundation of Tier 1, and Tier 3 – Advanced features capabilities that comprise completion of the practices needed for a sound and sustainable program for managing patient demographic data across the health care lifecycle.
A sample of the PDDQ’s successive practices is presented below, extracted from the Process Area Data Quality Planning. The Process Area purpose, introduction and contextual information for each question are not included here.
How the PDDQ is Intended to be Utilized
The Data Quality Coordinator, designated by the health care organization, is intended to serve as the project manager for the evaluation effort. This individual will communicate with stakeholders across the patient care lifecycle and bring them together in a workshop format to achieve a consensus answer about current capabilities, starting with Tier 1 – Foundational. As a part of this collaborative effort, the DQC will prepare for the discussion-based evaluation by requesting that work products are gathered in advance. This will facilitate the group’s consensus on evidence, e.g. “We are following this process and this is the documentation we use.”
Armed with the results of the evaluation, the organization can precisely identify the areas requiring attention and effort. The evaluation can be conducted internally, or the organization may choose to work with an external consultant facilitator to ensure consistent application of the framework.
We strongly recommend that the PDDQ evaluation is not addressed as a one-person effort, even in a small practice. There is typically no single individual who knows every detail of how patient demographic data is captured, managed, monitored, reported, and aggregated across the patient care life cycle. The organization will get better results and enhance stakeholder knowledge if the current practices are discussed as a group.
Health care data management consultants can employ the PDDQ for their client organizations as a powerful tool to quickly identify gaps, leverage accomplishments, focus priorities, and develop an improvement road map with the confidence that all factors have been examined and that consensus has been reached. That is the key to engaging stakeholders and greatly facilitates the adoption of improved processes that positively impact the patient data.
Scoring the Evaluation
Each question within a Process Area has three possible answers:
- Full – the organization’s consensus is that it is performing the practice indicated by the question – score = 1
- Partial – the consensus is that portions of the practice are being performed (examples are captured) – score = .5
- None – the consensus is that the practice is not currently being performed – score = 0
Each question or questions within each Tier must be answered Full to earn a Tier score of Full (1). Question responses are not weighted, because the PDDQ assumes that each Category and Process Area is important for an organization to assess their capabilities in managing patient demographic data. Note that it is typical for an organization to score higher in some areas and lower in others.
How Do I Access the PDDQ?
The PDDQ and evaluation scoring tool are available at the following location here.
A condensed version of the PDDQ, the Ambulatory Guide, contains a core set of questions aimed at very small health care practices, to help them get started in improving data quality. It is available at the following location here.
The link to the HHS ONC webinar announcing and introducing the PDDQ is available here.
In part two we covered what is evaluated as part of the framework, how the framework is intended to be used and how you can access the framework.
How the CMMI Institute Can Help
If a health care organization would like assistance in evaluating its data quality practices, CMMI Institute offers a PDDQ Evaluation service based on their highly successful approach that helps organizations implement the DMM’s processes and capabilities. Assistance is provided to the organization to prepare for the PDDQ Evaluation, stakeholder selection, work product gathering, setting up the evaluation workshop, and selecting supplementary interviewees. CMMI Institute facilitates the PDDQ evaluation on-site at your location, reviews the work products, conducts supplementary interviews, and finally develops a report highlighting needed improvements and a recommended sequential plan of initiatives to rapidly enhance capabilities. The approach delivers actionable results within three weeks, leading directly to the implementation phase. If your organization would like assistance in employing the PDDQ, please contact info@cmmiinstitute.com.
A link to CMMI Institute’s PDDQ resources is available here.
—–
About Jim Halcomb
Jim Halcomb, CMMI Institute’s DMM Practice Lead, has deep and diverse global data management experience in financial institutions, exchanges, and financial regulators. He led the development of data management best practices for the EDM Council, and was a primary author of the CMMI’s Data Management Maturity Model.